In the previous topic, we discussed how to make block elements floating as well as how to instruct the layout of the control to position blocks relative to pages when the control uses a paging view. Those features closely mimic the HTML properties for block layout. One of the areas where HTML falls behind in terms of features compared to traditional text processing and page authoring programs is the ability to position blocks relative to pages as well as to specify how floating blocks should affect inline content when it enters an area occupied by a floating block. Those shortcomings in HTML are addressed in NOV Rich Text for .NET.
The following properties are applied only to blocks that do not have intrinsic positioning - this includes paragraphs, tables, group blocks, and shape blocks. Block positioning properties are not regarded for root blocks, sections, table rows, and cells.
Horizontal and Vertical Block Anchor
By default, all blocks present in the content are laid out using the normal flow layout (with the exception of table cells). In this layout, each block is positioned vertically after the previous block in the content tree. In many cases when you want to produce truly dynamic layouts this type of layout is not sufficient to address all the possible positions of the block. The HorizontalAnchor and VerticalAnchor properties of the block allow you to specify how the block is positioned horizontally and vertically.
Horizontal Anchor
The horizontal anchor controls how the block is positioned horizontally by defining a range of x coordinates which the block uses to position itself. The horizontal anchor is controlled from the HorizontalAnchor property which accepts values from the ENHorizontalAnchor enum. The following table lists the available options:
| ENHorizontalAnchor |
Description |
| Flow |
Block uses normal flow. In this case, the block is positioned horizontally relative to the containing block x range. |
| Margin |
In this mode the block is positioned relatively to the margin of the page that contains the block. |
| Page |
In this mode the block is positioned relative to the page that contains the block. |
| LeftMargin |
Specifies that the horizontal positioning shall be relative to the left margin of the page that contains the block. |
| RightMargin |
Specifies that the horizontal positioning shall be relative to the right margin of the page. |
| InsideMargin |
Specifies that the horizontal positioning shall be relative to the inside margin of the current page (the left margin on odd pages, right on even pages). |
| OutsideMargin |
Specifies that the horizontal positioning shall be relative to the outside margin of the current page (the right margin on odd pages, left on even pages). |
| Ancestor |
In this mode the block is positioned relative to the first ancestor block that has the AllowAnchoredDescendantBlocks property set to true. In the absence of such block, the block is positioned relative to its root block. |
Vertical Anchor
Similarly, the vertical anchor defines a range of y values relative to which the block is positioned. It is controlled from the VerticalAnchor property accepting values from the ENVerticalAnchor enum:
| ENVerticalAnchor |
Description |
| Flow |
Block uses normal flow. In this case, the block is positioned vertically relative to the first previous block bottom with Flow vertical anchor. |
| Margin |
In this mode the block is positioned relatively to the margin of the page that contains the block. |
| Page |
In this mode the block is positioned relatively to the page that contains the block. |
| TopMargin |
In this mode the block is positioned relatively to the top margin of the page that contains the block. |
| BottomMargin |
In this mode the block is positioned relatively to the bottom margin of the page that contains the block. |
| InsideMargin |
In this mode the block is positioned relative to the inside margin of the page that contains the block (the top margin on odd pages, bottom on even pages). |
| OutsideMargin |
In this mode the block is positioned relatively to the outside margin of the page that contains the block (the bottom margin on odd pages, left on even pages). |
| Ancestor |
In this mode the block is positioned relatively to the first ancestor block top that has the AllowAnchoredDescendantBlocks property set to true. In the absence of such block the block is positioned relative to its root block. |
The following code snippet shows how to place a block at the left top of the block containing the page in print layout:
| Setting Block Horizontal and Vertical Anchors |
Copy Code
|
someBlock.HorizontalAnchor = ENHorizontalAnchor.Page;
someBlock.VerticalAnchor = ENVerticalAnchor.Page;
|
Setting the vertical block anchor to Page or Ancestor removes the block from the flow. Subsequent blocks with vertical anchor flow will be layout against the first block with flow vertical anchor preceding this block.
Horizontal and Vertical Block Alignment
When you define the reference x and y ranges against which the block is positioned you can further specify how the block is aligned relative to those ranges. This is achieved from the HorizontalBlockAlignment and VerticalBlockAlignment properties.
Horizontal Alignment
The horizontal alignment is controlled from the HorizontalBlockAlignment property - it accepts values from the ENHorizontalBlockAlignment enum:
| ENHorizontalBlockAlignment |
Description |
| Left |
The block is aligned to the left of the reference x range |
| Center |
The block is centered relative to the reference x range |
| Right |
The block is aligned to the right of the reference x range |
Vertical Alignment
The vertical alignment is controlled from the VerticalBlockAlignment property - it accepts values from the ENVerticalBlockAlignment enumeration:
| ENVerticalBlockAlignment |
Description |
| Top |
The block is aligned to the top of the reference y range |
| Center |
The block is centered relative to the reference y range |
| Bottom |
The block is aligned to the bottom of the reference y range |
The following code snippet shows how to center a block relative to the block's containing page in print layout:
| Setting Block Horizontal and Vertical Alignment |
Copy Code
|
someBlock.HorizontalAnchor = ENHorizontalAnchor.Page;
someBlock.VerticalAnchor = ENVerticalAnchor.Page;
someBlock.HorizontalBlockAlignment = ENHorizontalBlockAlignment.Center;
someBlock.VerticalBlockAlignment = ENVerticalBlockAlignment.Center;
|
Vertical block alignment is ignored in case the vertical block anchor is set to ENVerticalAnchor.Flow (which is the default).
Horizontal and Vertical Offset
After the block position is determined from the Anchor/Alignment properties you can further apply an additional offset in the horizontal and vertical direction using the XOffset and YOffset properties.
| Setting Block X and Y Offset |
Copy Code
|
someBlock.XOffset = 10;
someBlock.YOffset = 15;
|
The WrapMode property of the block allows you to specify whether the block will be removed from the flow and whether it will present an obstacle for inline content for other blocks that have inline content, which resides in the area occupied by the block. The following table lists the available options:
| ENWrapMode |
Description |
| None |
The block does not use wrapping |
| Before |
Block allows inline content to flow only before its left edge. Block is removed from the flow. |
| After |
Block allows inline content to flow only after its right edge. Block is removed from the flow. |
| Parallel |
Block allows inline content to flow before its left edge and after its right edge. Block is removed from the flow. |
| Through |
Block allows inline content to flow inside its area. Block is removed from the flow. |
When the block vertical anchor is set to Flow and you set a block wrap mode to Before, After, or Parallel the block will choose a block position that does not overlap with other floating blocks that also have a vertical anchor set to Flow.
How to Implement Normal Left and Right Floating Blocks just like in HTML
HTML allows blocks to float to the left or right side of their container block. This is achieved with the following property configuration:
| HTML Float Mode |
Equivalent Settings |
| Normal |
| Setting Block Flow to Normal |
Copy Code
|
// Normal
someBlock.HorizontalAnchor = ENHorizontalAnchor.Flow;
someBlock.HorizontalBlockAlignment = ENHorizontalBlockAlignment.Left;
someBlock.VerticalAnchor = ENVerticalAnchor.Flow;
someBlock.VerticalBlockAlignment = ENVerticalBlockAlignment.Top;
someBlock.WrapMode = ENWrapMode.None;
|
|
| Left |
| Setting Block Flow to Left |
Copy Code
|
// Left
someBlock.HorizontalAnchor = ENHorizontalAnchor.Flow;
someBlock.HorizontalBlockAlignment = ENHorizontalBlockAlignment.Left;
someBlock.VerticalAnchor = ENVerticalAnchor.Flow;
someBlock.VerticalBlockAlignment = ENVerticalBlockAlignment.Top;
someBlock.WrapMode = ENWrapMode.After;
|
|
|
| Right |
| Setting Block Flow to Right |
Copy Code
|
// Right
someBlock.HorizontalAnchor = ENHorizontalAnchor.Flow;
someBlock.HorizontalBlockAlignment = ENHorizontalBlockAlignment.Right;
someBlock.VerticalAnchor = ENVerticalAnchor.Flow;
someBlock.VerticalBlockAlignment = ENVerticalBlockAlignment.Top;
someBlock.WrapMode = ENWrapMode.Before;
|
|
How to Implement Relative Positioned Blocks like in HTML
Relatively positioned blocks serve two purposes - the first one is to act as anchors (or coordinate system parents) for absolutely positioned blocks and the second one is to be able to move a block relatively to its original flow position. In NOV RichText Editor these two tasks are achieved by setting the AllowAnchoredDescendantBlocks property to true and by modifying the XOffset and YOffset properties respectively.
| Setting Block Relative Position Properties |
Copy Code
|
someBlock.AllowAnchoredDescendantBlocks = true;
someBlock.XOffset = 10;
someBlock.YOffset = -10;
|
How to Implement Absolute Positioned Blocks like in HTML
Absolutely positioned blocks in HTML can be aligned relative to the first parent block which uses either relative or absolute position. In NOV RichText absolutely positioned blocks are achieved by setting the AllowAnchoredDescendantBlocks property to true of the ancestor block relative to which you want to position the block and then modify the horizontal and vertical block anchors. The following code snippet shows how to implement an absolutely positioned paragraph contained in a group block:
| Setting Block Relative Position Properties |
Copy Code
|
// create a section
NSection section = new NSection();
NGroupBlock groupBlock = new NGroupBlock();
groupBlock.PreferredHeight = new NMultiLength(ENMultiLengthUnit.Dip, 200);
groupBlock.Border = NBorder.CreateFilledBorder(NColor.Black);
groupBlock.BorderThickness = new NMargins(2);
groupBlock.AllowAnchoredDescendantBlocks = true;
// create an absolutely positioned paragraph
NParagraph absolutePositionedParagraph = new NParagraph("Absolutely Positioned Paragraph");
absolutePositionedParagraph.BackgroundFill = new NColorFill(ENNamedColor.Red);
absolutePositionedParagraph.HorizontalAnchor = ENHorizontalAnchor.Ancestor;
absolutePositionedParagraph.VerticalAnchor = ENVerticalAnchor.Ancestor;
absolutePositionedParagraph.XOffset = 100;
absolutePositionedParagraph.YOffset = 100;
// create normal positioned paragraphs
NParagraph normalPositionedParagraph1 = new NParagraph("Normal Positioned Paragraph 1");
normalPositionedParagraph1.BackgroundFill = new NColorFill(ENNamedColor.Green);
NParagraph normalPositionedParagraph2 = new NParagraph("Normal Positioned Paragraph 2");
normalPositionedParagraph2.BackgroundFill = new NColorFill(ENNamedColor.Green);
// add them to the group block
groupBlock.Blocks.Add(normalPositionedParagraph1);
groupBlock.Blocks.Add(absolutePositionedParagraph);
groupBlock.Blocks.Add(normalPositionedParagraph2);
section.Blocks.Add(groupBlock);
m_RichText.Content.Sections.Clear();
m_RichText.Content.Sections.Add(section);
|
This code produces the following image:
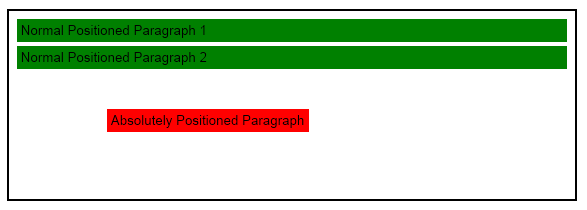
Notice how the absolutely positioned paragraph is taken out of the flow. This causes to the second normal flow paragraph (normalPositionedParagraph2) in the block to be adjacent to the first one (normalPositionedParagraph1). Also when using a horizontal anchor different from ENHorizontalAnchor.Flow, the block width will be computed based on the desired width instead of the parent content width, similar to HTML.

